This topic explains how content may be compressed by your web servers.
Setup
Origin server compression requires the following setup:
-
The request must include an Accept-Encoding header set to one or more of the following compression types:
- gzip
- deflate
- bzip2
- brRepresents Brotli compression.
This header allows the user agentRefers to software that acts on behalf of a user. For example, a web browser (e.g., FireFox, Chrome, and Internet Explorer) is a user agent. A web browser will make HTTP/HTTPS requests based on user actions (e.g., requesting a web site or clicking a link). to indicate which compression methods it supports to the origin server.
- The web servers associated with your customer origin must support the compression method defined within the Accept-Encoding request header.
How It Works (HTTP Large and HTTP Small)
This section explains the workflow through which content may be compressed by your web servers for HTTP Large and HTTP Small traffic.
Basic Workflow
A client may request compressed content from your web servers. If a supported compression type is requested, then compressed content will be served from your web servers and eventually be cached on our edge servers.
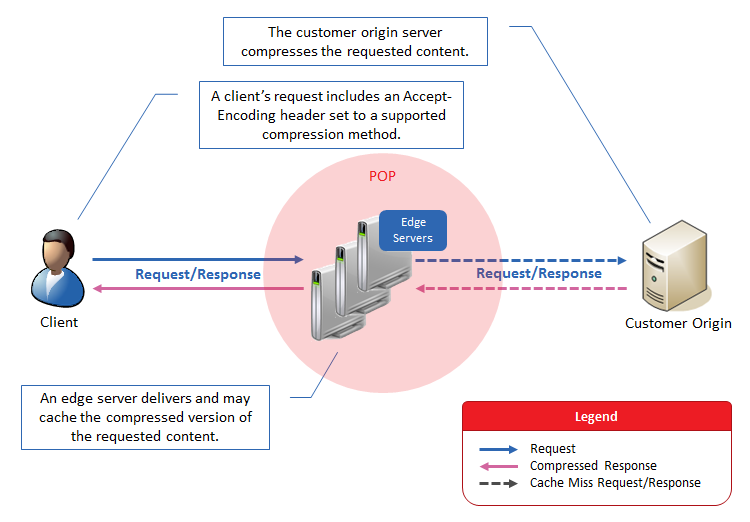
Detailed Workflow
Detailed information on how requests are handled with regards to origin server compression is provided below.
-
Requester: A user submits a request for content. The manner in which this request is handled by our edge servers depends on whether the request includes the Accept-Encoding header.
Accept-Encoding Header Description Set to a supported compression method.
This type of request will be handled as described in step 2.
Set to an unsupported compression method.
Our edge servers will always retrieve the requested content from your customer origin server.
This type of request will not be cached and therefore will be handled as described in step 2's Cache Miss bullet item.
Missing
This type of request will be served in an uncompressed format as described by either the Cache Miss or the Uncompressed Cache Hit bullet item in step 2.
-
POP: An edge server on the POP closest to the client will check to see if the requested content has been cached and if it still has a valid TTL.
- Cache Miss: If a cached version of the requested content is not found, then the request will be forwarded to an origin server. Proceed to step 3.
- Cache Hit & Matching Compression Method: An edge server will immediately deliver the compressed content to the client.
- Cache Hit & Different Compression Method: If the client requests a supported compression method that is different from the one used by the initial request, then an edge server will transcode the asset to the requested compression method and then deliver it.
-
Uncompressed Cache Hit: If the initial request caused the asset to be cached in an uncompressed format, then a check will be performed to see whether the request is eligible for edge server compression.
- Eligible: The requested asset will be compressed as indicated in the Edge Server Compression topic and then delivered to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached.
- Ineligible: An edge server will immediately deliver the uncompressed content to the client.
-
Origin Server: The manner in which the origin server will handle the request depends on whether both the CDN and your web servers support the compression method specified in the Accept-Encoding header.
CDN Customer Origin
Request Workflow Supported compression method
Supported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will compress the asset and send it to an edge server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the compressed asset to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached.
Supported compression method
Unsupported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve an uncompressed asset to an edge server.
-
Edge Server: It will:
- Serve the uncompressed asset to the client.
-
Check to see whether the request is eligible for edge server compression.
- Eligible: The requested asset will be compressed as indicated in the Edge Server Compression topic and then delivered to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached.
- Ineligible: An edge server will immediately deliver the uncompressed content to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the uncompressed asset is eligible to be cached.
Unsupported compression method
Supported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve a compressed asset to an edge server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the compressed asset to the client. However, it will not cache it.
Unsupported compression method
Unsupported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve an uncompressed asset to an edge server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the uncompressed asset to the client. However, it will not cache it.
How It Works (ADN)
This section explains the workflow through which content may be compressed by your web servers for ADN traffic.
Basic Workflow
A client may request compressed content from your web servers. If a supported compression type is requested, then compressed content will be served from your web servers. If the request is eligible for caching, then it will eventually be cached on an ADN Gateway server and our edge servers.
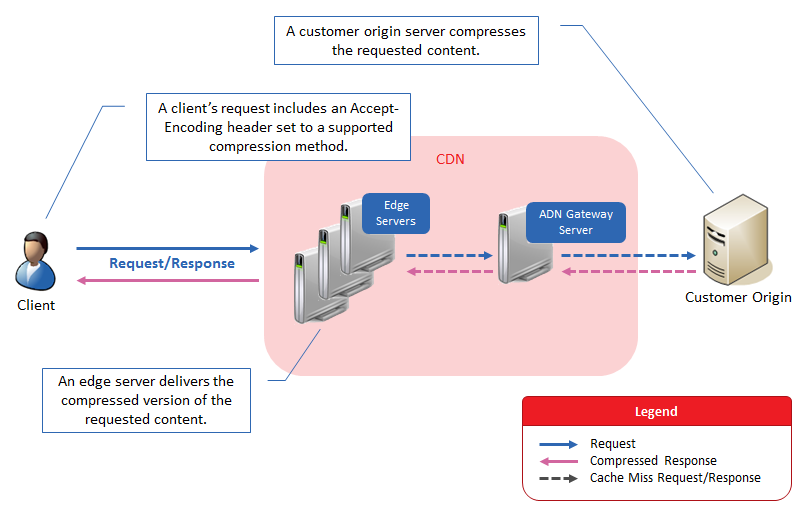
Detailed Workflow
Detailed information on how requests are handled with regards to origin server compression is provided below.
-
Requester: A user submits a request for content. The manner in which this request is handled by our edge servers depends on whether the request includes the Accept-Encoding header.
Accept-Encoding Header Description Set to a supported compression method.
This type of request will be handled as described in step 2.
Set to an unsupported compression method.
Our edge servers will always retrieve the requested content from your customer origin server.
This type of request will not be cached and therefore will be handled as described in step 2's Cache Miss bullet item.
Missing
This type of request will be served in an uncompressed format as described by either the Cache Miss or the Uncompressed Cache Hit bullet item in step 2.
-
POP: An edge server on the POP closest to the client will check to see if the requested content has been cached and if it still has a valid TTL.
- Cache Miss: If a cached version of the requested content is not found, then the request will be forwarded to an origin server. Proceed to step 3.
- Cache Hit & Matching Compression Method: An edge server will immediately deliver the compressed content to the client.
- Cache Hit & Different Compression Method: If the client requests a supported compression method that is different from the one used by the initial request, then an edge server will transcode the asset to the requested compression method and then deliver it.
-
Uncompressed Cache Hit: If the initial request caused the asset to be cached in an uncompressed format, then a check will be performed to see whether the request is eligible for edge server compression.
- Eligible: The requested asset will be compressed as indicated in the Edge Server Compression topic and then delivered to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached on both the respective edge server and ADN Gateway server.
- Ineligible: An edge server will deliver the uncompressed content to the client.
By default, content requested through the ADN platform will not be cached and therefore should result in a cache miss.
-
Origin Server: The manner in which the origin server will handle the request depends on whether both the CDN and your web servers support the compression method specified in the Accept-Encoding header.
CDN Customer Origin
Request Workflow Supported compression method
Supported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will compress the asset and send it to an edge server via anADN Gateway server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the compressed asset to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached on both the ADN Gateway and edge server.
Supported compression method
Unsupported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve an uncompressed asset to an edge server via anADN Gateway server.
-
Edge Server: It will:
- Serve the uncompressed asset to the client.
-
Check to see whether the request is eligible for edge server compression.
- Eligible: The requested asset will be compressed as indicated in the Edge Server Compression topic and then delivered to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the compressed asset is eligible to be cached on both the respective edge server and ADN Gateway server.
- Ineligible: An edge server will immediately deliver the uncompressed content to the client. Your caching policy dictates whether the uncompressed asset is eligible to be cached on both the respective edge server and ADN Gateway server.
Unsupported compression method
Supported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve a compressed asset to an edge server via anADN Gateway server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the compressed asset to the client. However, it will not cache it.
Unsupported compression method
Unsupported compression method
- Customer Origin: It will serve an uncompressed asset to an edge server via anADN Gateway server.
- Edge Server: It will serve the uncompressed asset to the client. However, it will not cache it.
Edgecast CDN