Set up support for HTTPS content delivery through the following procedure:
- Request a TLSSecure Socket Layer / Transport Layer Security. Refers to protocols that encrypt traffic for the purpose of delivery over HTTPS. Although traffic will be encrypted using the TLS protocol, SSL is mentioned here as a point of reference for readers that are more familiar with this legacy technology. certificate and wait until it has been installed on our network.
-
Configure the CDN to communicate with your web servers over HTTPS.
- Configure your firewall to allow our network to communicate with your web servers.
- Create an edge CNAME configuration for the hostname associated with the TLS certificate.
- Update a CNAME recordA Canonical Name (CNAME) record is used to indicate that a hostname is an alias of another hostname. A CNAME record must be registered on a Domain Name System (DNS). This term should not be confused with edge CNAME. within your DNS zone to switch traffic over to our service.
PCI Only: Setting up a customer origin group for a site whose traffic must be served over a Payment Card Industry-certified (PCI) network requires assistance. Contact our technical customer support prior to setup.
TLS Certificate
Support for HTTPS content delivery requires that a TLS certificate be installed on our network.
Navigate to the Certificate Provisioning System page.
Click Add Certificate and then submit a request for a TLS certificate.
Prove your control over each Subject Alternative Name (SAN) defined in the certificate via a Domain Control Validation (DCV) method (i.e., email, DNS TXT, or DNS CNAME).
OV and EV Certificate: Validate your organization by following the directions provided by the Certificate Authority (CA) via phone or email.
Wait until the CA has validated your request.
Upon validation, your certificate will be issued and installed on our network. Additionally, a target CNAME will be generated . You will need to use this target CNAME during DNS setup.
Configure the CDN to Communicate with your Web Servers
Before the CDN may serve HTTPS traffic from your web servers, it must be informed where they are located via a customer originRefers to a CDN configuration that identifies one or more web servers that will serve as the source from which content may be delivered via the CDN. configuration.
Load the Customer Origin Page
A customer origin configuration allows the CDN to serve traffic from your web server(s).
Navigate to the Customer Origin page.
The Customer Origin page will immediately show a blank customer origin configuration.

IP Preference
By default, our CDN service will resolve hostnames to IPv4.
Directory Name
Assign a unique name to a customer origin configuration. This name will be incorporated into the CDN URLA system-defined URL that points to a CDN hostname. A CDN URL allows content delivery via our network. Simplify your CDN setup by also creating an edge CNAME configuration which potentially allows you to deliver traffic via the CDN using the same links as your current setup. generated for this customer origin.
Sample CDN URL for a customer origin called "marketing":
In the Directory Name option, type an alphanumeric word or phrase (e.g., marketing).

The CDN service must be informed where to find each web server associated with this customer origin configuration. This step involves providing one or more IP addresses or hostnames that point to your web servers.
Clear the HTTP Edge Protocol option.
Mark the HTTPS Edge Protocol option.
In the Hostname or IP Address option, type the hostname or IP address of the server where your data resides. Append a colon and the port through which communication will take place (e.g., https://marketing.mydomain.com:443).
Click Add which appears directly to the right of the Hostname or IP Address option.
Configuring CAN Gateway Servers
A CAN Gateway server optimizes the communication path between the edge of our network and your web servers (i.e., customer origin servers). Setting up CAN Gateway servers requires testing connectivity between each CAN Gateway server and the servers associated with the customer origin configuration (as defined in the Web Server Information step).
Upload a 5 KB asset to each web server associated with this customer origin configuration.
Multiple Servers: Make sure to upload this sample asset to the same location on each web server.
In the Validation Path option, type a URL that points to the asset uploaded in the previous step. Make sure that the hostname specified in this URL matches the value defined in the HTTP Host Header option.
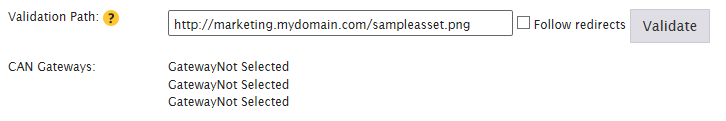
Click Validate. If the result returns 200 OK for all hostnames/IP addresses, then proceed to the next step.
Create the customer origin by saving your changes.
Click Add to save your customer origin configuration.
Set up Firewall Access
The next step is to ensure that a firewall doesn't block the flow of traffic between your web servers and the CDN.
Configure your firewall to allow all of our IP blocks access to your server(s).
View our IP blocks within the Whitelist IP Blocks section of the Customer Origin page.
Create an Edge CNAME Configuration
HTTPS traffic may only be served via an edge CNAME URLThis type of URL takes advantage of an edge CNAME configuration and a CNAME record to provide a friendlier alternative to a CDN URL. An edge CNAME URL is specific to the platform from which it was configured.. Do not attempt to serve HTTPS traffic using the CDN URL generated for the customer origin created in this tutorial.
Create an edge CNAMERefers to the mapping of a CNAME record to a directory on a CDN or customer origin server. The purpose of this mapping, which is only used by our CDN, is to establish a user-friendly alias for content served through the CDN. It relies upon your CNAME record being mapped to a CDN hostname via a DNS service provider. configuration that will direct traffic to the customer origin created in this tutorial. This setup allows traffic to be shifted to the CDN by simply updating a CNAME recordA Canonical Name (CNAME) record is used to indicate that a hostname is an alias of another hostname. A CNAME record must be registered on a Domain Name System (DNS). This term should not be confused with edge CNAME. to point to a CDN hostnameRefers to a system-defined hostname that is specific to your customer account and a CDN service..
Navigate to Edge CNAME Settings
An edge CNAME configuration must be created on the same platform as the customer origin that was created earlier in this tutorial.
Navigate to the Edge CNAMEs page corresponding to the platform to which the desired customer origin was added.
Name an Edge CNAME
An edge CNAME configuration should be named after the hostname defined in the requested TLS certificate.
This name should be specified in lower-case letters and should not include a protocol (i.e., https://).
In the New Edge Cname option, type the hostname defined in the requested TLS certificate.

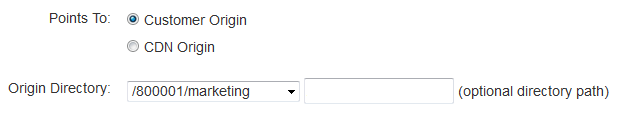
Identify a Customer Origin
This step defines the customer origin from which requests to this edge CNAME will be served.
In the Points to option, verify that "Customer Origin" is selected.
In the Origin Directory option, select the recently created customer origin configuration.
Save Changes
Create an edge CNAME by saving your changes.
Click Add.
An edge CNAME that points to a customer origin configuration should appear at the top of the Edge CNAMEs page.
Wait an hour to allow your changes to be applied before proceeding beyond this point.
Update a CNAME Record via a DNS Service Provider
Switching traffic over to our CDN service requires updating a CNAME record to point to an edge CNAME .
Load your DNS service provider's portal.
Find the CNAME record corresponding to the edge CNAME created above (e.g., cdn1.mydomain.com).
Update the CNAME's value to resolve to the CDN hostname provided by your CDN account manager for the TLS certificate requested earlier in this tutorial.
Once this DNS change takes effect, traffic will shift to our CDN service.
More Information
Edgecast CDN